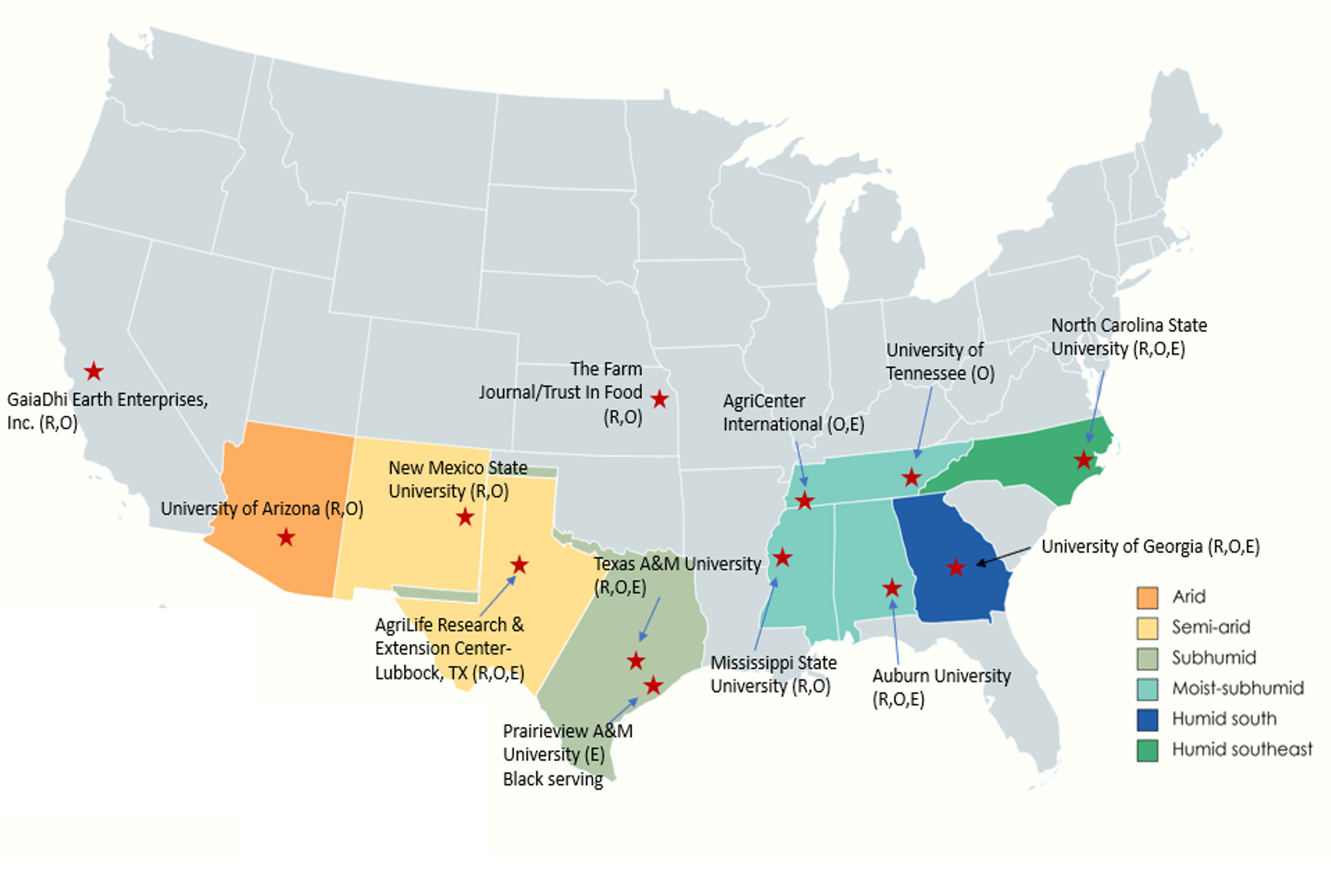
Multi-State Partnership
American Cotton
The sustainability of US cotton production is pivotal to agricultural sustainability in theSouthern US. Protecting and improving soil health, reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions,and enhancing input use efficiency are central to improving the sustainability of cotton in theface of changing climatic conditions.
Background:
•Cotton is a major crop in the U.S., valued at $7 billion annually and covering ~12.5 million acres.
•Sustainability is challenged by intensive tillage, soil degradation, and pesticide resistance across the Cotton Belt.
•Adoption of conservation tillage, cover crops, living mulches, and other regenerative practices can enhance soil health and carbon sequestration.
•Integrating AI/ML-based precision practices can reduce input use, lower GHG emissions, and move U.S. cotton towards a sustainable future.
A USDA-NIFA Sustainable Agriculture Systems-Coordinated Agriculture Project (SAS-CAP) addresses these challenges in different ecoregions across the U.S. Cotton Belt, with multi-state and multi-institutional partnerships
Cotton by the Numbers
Cotton is an economically important crop in the United States (US), with an annual economic value of $7 billion (USDA-ERS 2022). The US is also the world’s leading exporter of cotton, contributing to about 35% of global cotton exports. In 2022, cotton was planted on 12.5 million acres in the US, with Texas, Georgia, Mississippi, Arkansas, Oklahoma, North Carolina, Missouri, Tennessee, and Alabama being the major cotton-producing states in the US Cotton Belt. Texas accounted for 57% of all cotton planted in the US in 2022 (USDA-NASS 2022a).
why
Project Goals
The overall hypothesis of the proposed project is that regenerative production practices, including those that allow for a reduction in tillage for weed control, use of advances in digital technologies for resources input management will transform current US cotton production into a more climate-smart, resilient, and sustainable operation. The long-term goal of the proposed research is to apply improved precision management practices to enable enhanced carbon sequestration and reduced greenhouse gas emission, pest control, and nutrient and water management; and to address labor challenges, steward land, create new market opportunities, and ensure a sustainable supply of climate-smart cotton.
when
where
Texas A&M Agrilife
Heep Center
370 Olsen Blvd.
College Station, TX 77843